10. Design a React application featuring a class-based component that demonstrates the use of lifecycle methods to interact with an external API. The component should fetch and update data dynamically based on user interactions or state changes. Use the componentDidMount lifecycle method to fetch data from an API when the component is initially rendered. Display the fetched data in a structured format, such as a table or list. Use the componentDidUpdate lifecycle method to detect changes in the component’s state or props. Trigger additional API calls to update the displayed data based on user input or actions (e.g., filtering, searching, or pagination). Implement error handling to manage issues such as failed API requests or empty data responses. Display appropriate error messages to the user when necessary. Allow users to perform actions like filtering, searching, or refreshing the data. Reflect changes in the displayed data based on these interactions.
Step 1: Create a New React Application
- First, you need to create a new React app using below command. Open your terminal and run:
npx create-react-app data-fetcherThis will set up a new React project in a folder called data-fetcher. After the installation is complete, navigate to the project directory:
cd data-fetcherStep 2: Update src/App.js:
- Navigate to the
srcfolder in the file explorer on the left-hand side of VSCode. - Open the
App.jsfile (which contains the default template code). - Replace the content of
App.jswith the code provided for the data-fetcher. Here’s the code to replace insideApp.js:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
const API_URL = 'https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users';
class DataFetcher extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
data: [],
filteredData: [],
searchQuery: '',
error: null,
loading: false,
};
}
componentDidMount() {
this.fetchData();
}
fetchData = async () => {
this.setState({ loading: true, error: null });
try {
const response = await fetch(API_URL);
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error('Failed to fetch data');
}
const data = await response.json();
this.setState({ data, filteredData: data, loading: false });
} catch (error) {
this.setState({ error: error.message, loading: false });
}
};
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState) {
if (prevState.searchQuery !== this.state.searchQuery) {
this.filterData();
}
}
handleSearchChange = (event) => {
this.setState({ searchQuery: event.target.value });
};
filterData = () => {
const { data, searchQuery } = this.state;
if (searchQuery.trim() === '') {
this.setState({ filteredData: data });
} else {
const filteredData = data.filter((item) =>
item.name.toLowerCase().includes(searchQuery.toLowerCase())
);
this.setState({ filteredData });
}
};
renderError = () => {
const { error } = this.state;
return error ? <div className="error">{`Error: ${error}`}</div> : null;
};
render() {
const { filteredData, searchQuery, loading } = this.state;
return (
<div className="data-fetcher">
<h1>User Data</h1>
{this.renderError()}
<div className="search-bar">
<input
type="text"
value={searchQuery}
onChange={this.handleSearchChange}
placeholder="Search by name"
/>
</div>
{loading ? (
<div>Loading...</div>
) : (
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Email</th>
<th>City</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{filteredData.length > 0 ? (
filteredData.map((item) => (
<tr key={item.id}>
<td>{item.name}</td>
<td>{item.email}</td>
<td>{item.address.city}</td>
</tr>
))
) : (
<tr>
<td colSpan="3">No results found.</td>
</tr>
)}
</tbody>
</table>
)}
<button onClick={this.fetchData}>Refresh Data</button>
</div>
);
}
}
export default DataFetcher;Step 3: Update src/index.js:
- Replace the default content of
src/index.jswith this code to ensure the component is rendered in your application:
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client';
import './App.css';
import DataFetcher from './App';
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root'));
root.render(
<React.StrictMode>
<DataFetcher />
</React.StrictMode>
);Step 4: Modify the App.css
- You can adjust the styling if desired. For example, you can modify
App.cssto ensure the UI look good:
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
background-color: #f4f4f4;
}
button {
border-radius: 5px;
border: none;
cursor: pointer;
color: #fff;
font-weight: bold;
background: red;
margin-top: 20px;
padding: 10px;
}
.data-fetcher {
width: 80%;
margin: 0 auto;
padding: 20px;
background-color: #fff;
border-radius: 8px;
box-shadow: 0 4px 8px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
}
h1 {
text-align: center;
color: #333;
}
.search-bar {
margin: 20px 0;
text-align: center;
}
.search-bar input {
padding: 8px;
width: 60%;
font-size: 16px;
border: 1px solid #000;
border-radius: 4px;
}
table {
width: 100%;
margin-top: 20px;
border-collapse: collapse;
}
table th,
table td {
padding: 10px;
text-align: left;
border-bottom: 1px solid #ddd;
}
.error {
color: red;
text-align: center;
}Step 5: Start the Development Server
- In the terminal inside VSCode, run the following command to start the React development.
npm start- This will open your browser and navigate to
http://localhost:3000/. You should see your Counter Application up and running.
OUTPUT:
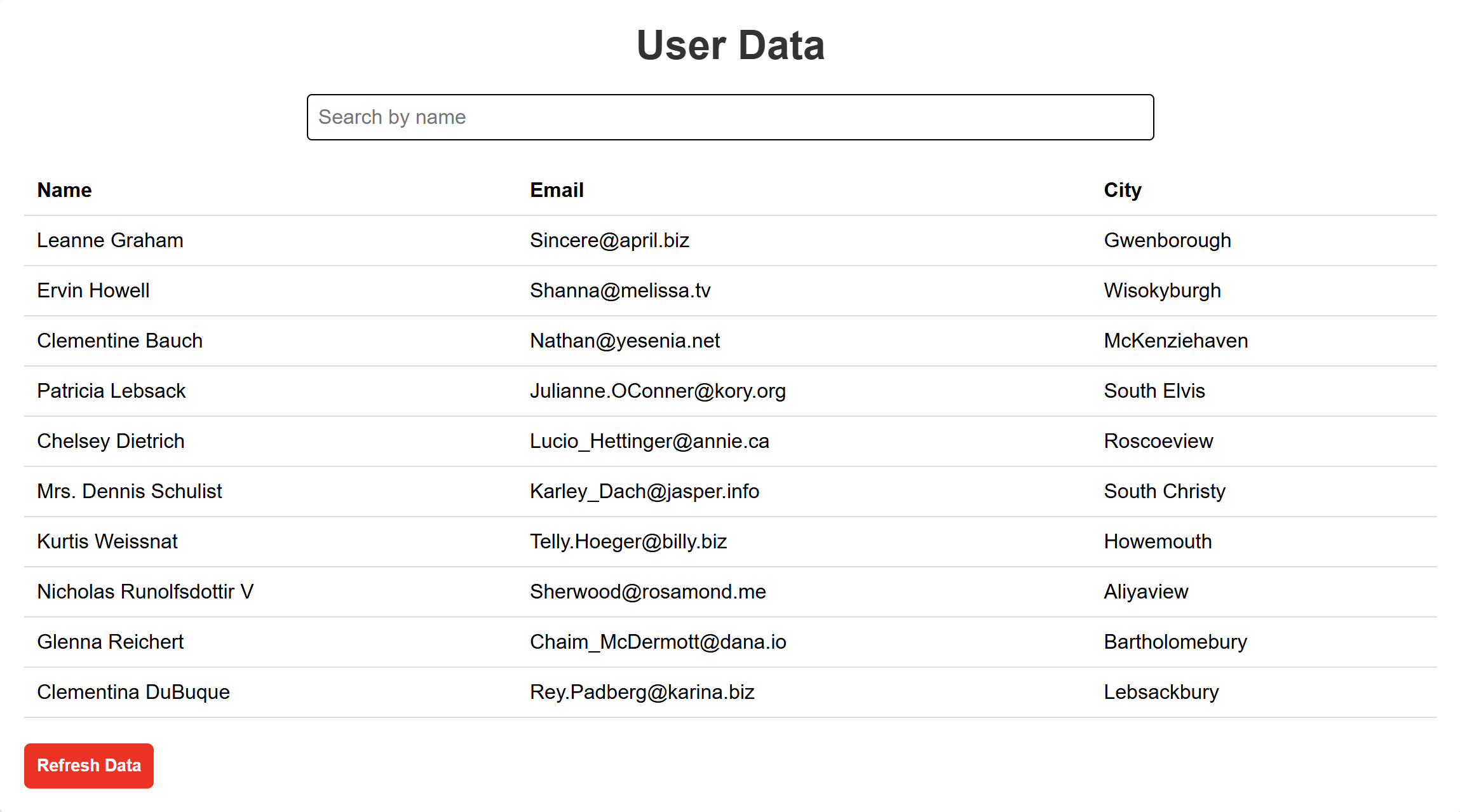
“Fixing the Module not found: Error: Can't resolve 'web-vitals' Error in React”
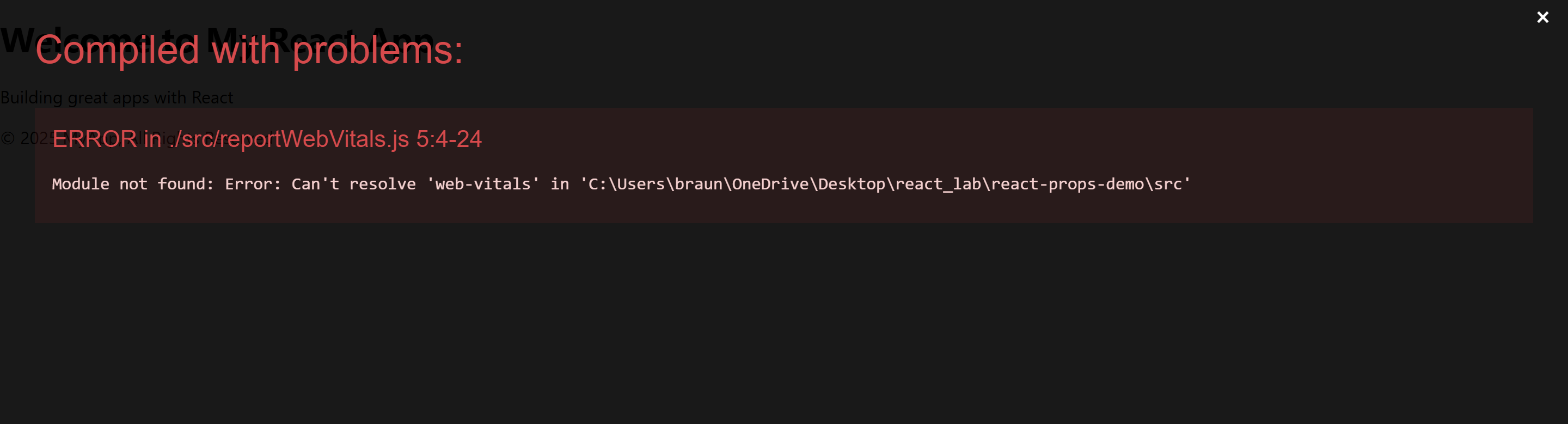
The error you’re seeing occurs because the web-vitals package, which is used for performance monitoring in a React app, is not installed by default in the project or has been removed. Since web-vitals is an optional package, you can safely resolve this issue by either installing the package or removing the code that imports it.
Option 1: Install the web-vitals package
If you want to keep the performance monitoring functionality and resolve the error, simply install the web-vitals package.
- In the terminal, navigate to your project folder (if not already there):
cd data-fetcher- Install
web-vitalsby running the following command:
npm install web-vitals- After installation is complete, restart the development server:
npm startThis should resolve the error, and your application should compile correctly.
Option 2: Remove the Web Vitals Code (If Not Needed)
If you don’t need performance monitoring and want to get rid of the error, you can safely remove the import and usage of web-vitals from your code.
- Open
src/reportWebVitals.jsand remove its contents or just comment out the code:
// import { reportWebVitals } from './reportWebVitals';
// You can safely remove the call to reportWebVitals or leave it commented out
// reportWebVitals();- Save the file, and the application should compile without the error. You can now continue developing your app.
