9. Design a React application that demonstrates the implementation of routing using the react-router-dom library. The application should include the Navigation Menu: Create a navigation bar with links to three distinct pages, Home, About, Contact. Develop separate components for each page (Home, About, and Contact) with appropriate content to differentiate them. Configure routes using react-router-dom to render the corresponding page component based on the selected link. Use BrowserRouter and Route components for routing. Highlight the active link in the navigation menu to indicate the current page.
Step 1: Create a New React Application
First, you need to create a new React app using below command. Open your terminal and run:
npx create-react-app my-routing-appThis will set up a new React project in a folder called my-routing-app. After the installation is complete, navigate to the project directory:
cd my-routing-appStep 2: Install react-router-dom
- In the terminal inside VSCode, install
react-router-dom:
npm install react-router-domStep 3: Set Up the Folder Structure
Create the folder structure. Here’s how you can organize the directories:
- Inside the
srcfolder:- Create a
componentsfolder. - Inside
components, createHome.js,About.js,Contact.js and Navbar.jsfiles. Copy below code and paste it into the different files.
- Create a
Home.js:
import React from 'react';
const Home = () => {
return (
<div>
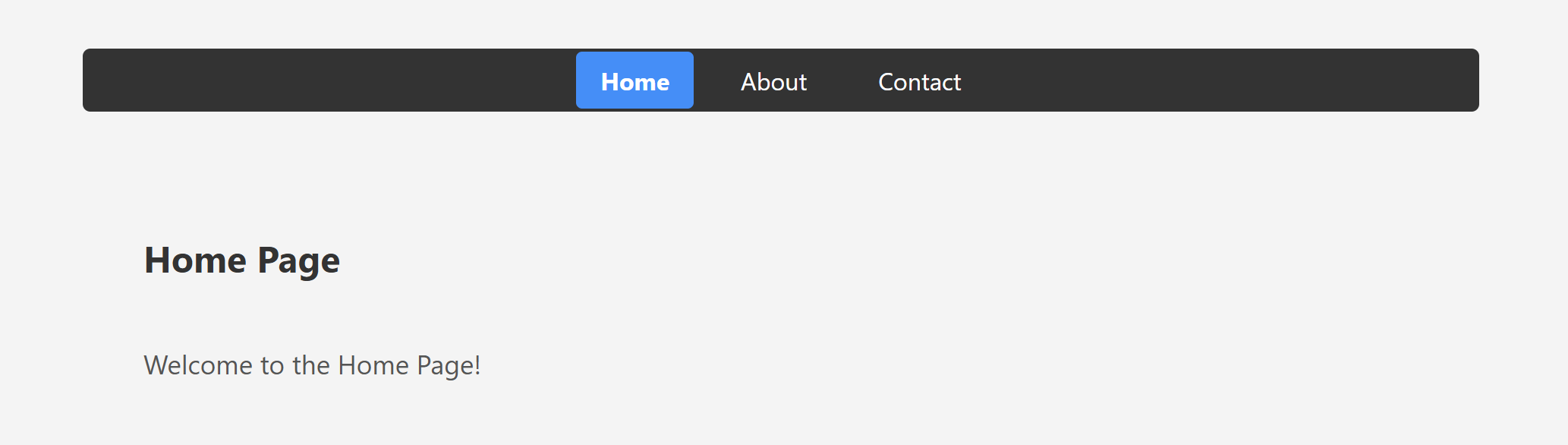
<h2>Home Page</h2>
<p>Welcome to the Home Page!</p>
</div>
);
};
export default Home;About.js:
import React from 'react';
const About = () => {
return (
<div>
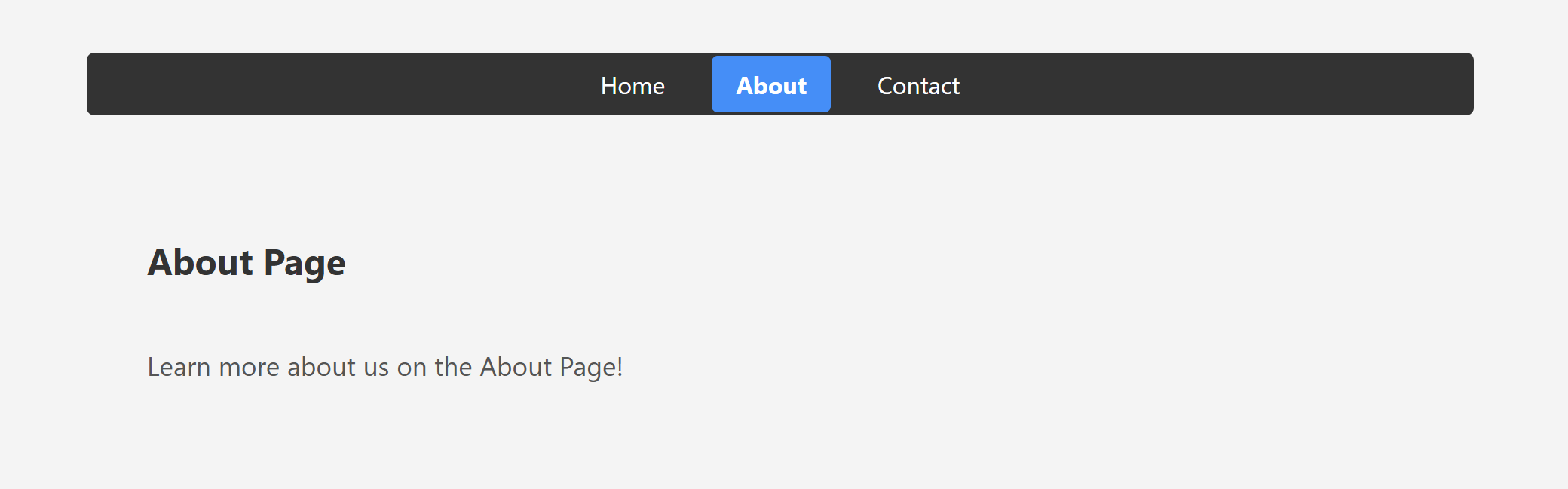
<h2>About Page</h2>
<p>Learn more about us on the About Page!</p>
</div>
);
};
export default About;Contact.js:
import React from 'react';
const Contact = () => {
return (
<div>
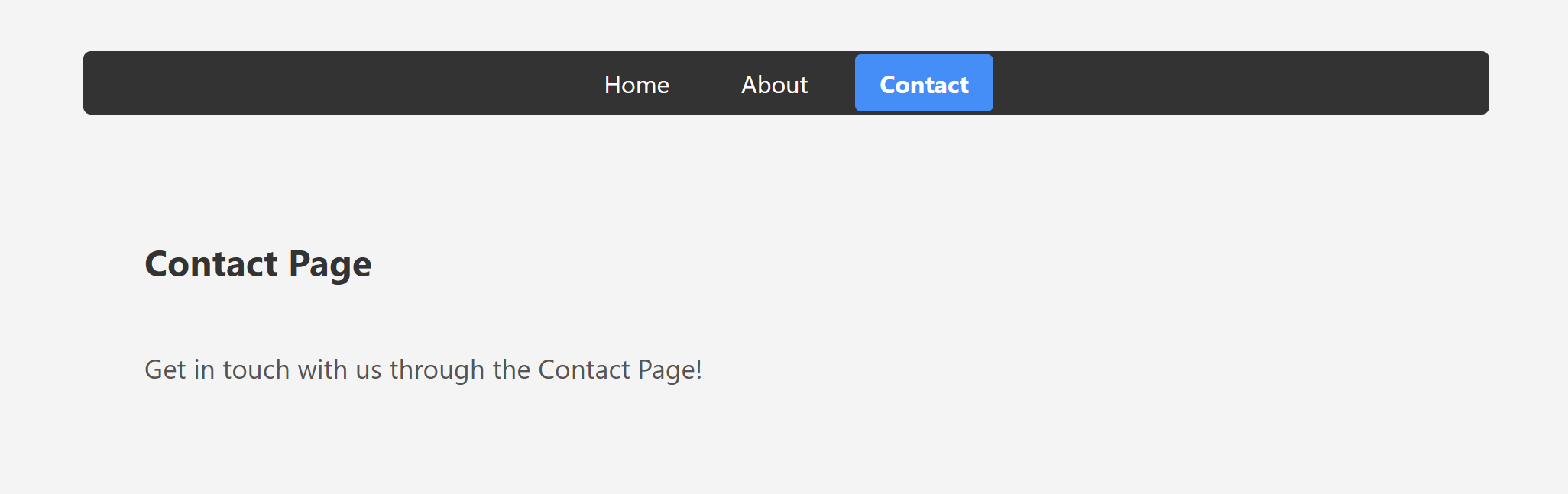
<h2>Contact Page</h2>
<p>Get in touch with us through the Contact Page!</p>
</div>
);
};
export default Contact;Navbar.js:
import React from 'react';
import { NavLink } from 'react-router-dom';
const Navbar = () => {
return (
<nav>
<ul>
<li>
<NavLink
to="/"
className={({ isActive }) => (isActive ? 'active' : '')}
>
Home
</NavLink>
</li>
<li>
<NavLink
to="/about"
className={({ isActive }) => (isActive ? 'active' : '')}
>
About
</NavLink>
</li>
<li>
<NavLink
to="/contact"
className={({ isActive }) => (isActive ? 'active' : '')}
>
Contact
</NavLink>
</li>
</ul>
</nav>
);
};
export default Navbar;Step 4. App Component(src/App.js):
In your src/App.js, import the Home.js, About.js, Contact.jsNavbar.js component and use it or copy the below code and paste it into the App.js file.
import React from 'react';
import { BrowserRouter as Router, Route, Routes } from 'react-router-dom';
import Navbar from './components/Navbar';
import Home from './components/Home';
import About from './components/About';
import Contact from './components/Contact';
import './App.css'
const App = () => {
return (
<Router>
<div>
<Navbar />
<div style={{ padding: '20px' }}>
<Routes>
<Route path="/" element={<Home />} />
<Route path="/about" element={<About />} />
<Route path="/contact" element={<Contact />} />
</Routes>
</div>
</div>
</Router>
);
};
export default App;Step 5: Add Styles(src/App.css)
Add some styles in src/App.css to make the layout nicer. Copy the below code and paste it into the App.css file.
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
background-color: #f4f4f4;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
div {
margin: 0 auto;
max-width: 960px;
padding: 20px;
}
h2 {
color: #333;
padding-bottom: 20px;
}
nav {
background-color: #333;
padding: 10px;
border-radius: 5px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
ul {
list-style: none;
display: flex;
gap: 15px;
justify-content: center;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
li {
display: inline;
}
a {
text-decoration: none;
color: white;
padding: 8px 16px;
border-radius: 4px;
}
a:hover {
background-color: #444;
}
a.active {
background-color: #1e90ff;
color: white;
font-weight: bold;
}
p {
color: #555;
font-size: 1.1rem;
line-height: 1.6;
}
Step 6: Set Up the Entry Point (index.js)
- Open
src/index.jsand ensure the entry point is correct:
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client';
import App from './App';
const rootElement = document.getElementById('root');
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(rootElement);
root.render(<App />);Step 7: Run the App
- Now that you’ve set up everything, go back to your terminal and run:
npm start- This will start your React app, and it should automatically open in your default browser at
http://localhost:3000.
OUTPUT:
“Fixing the Module not found: Error: Can't resolve 'web-vitals' Error in React”
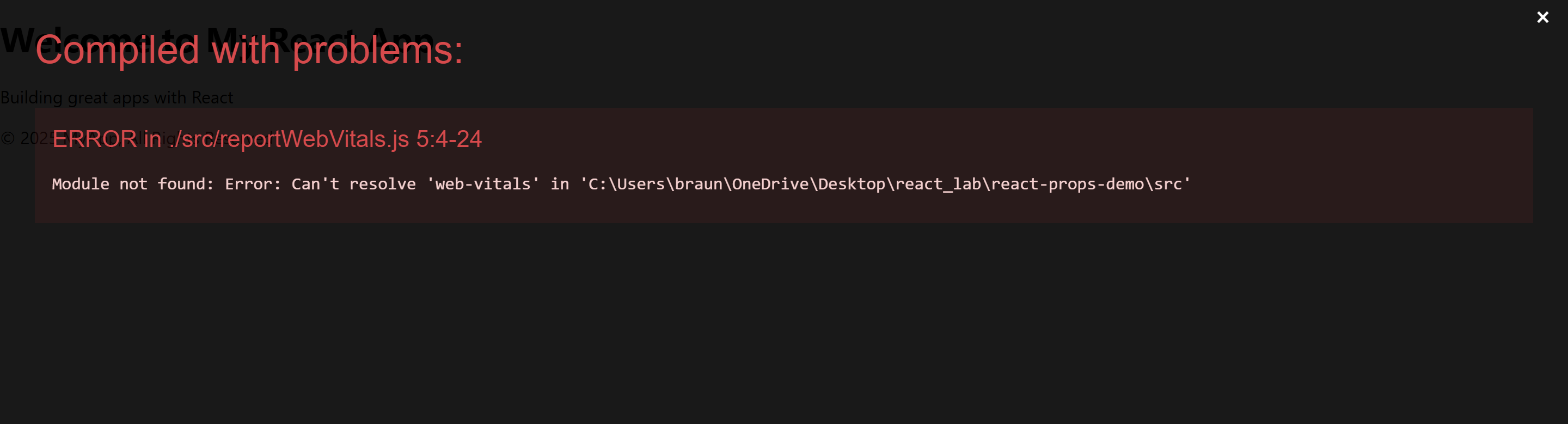
The error you’re seeing occurs because the web-vitals package, which is used for performance monitoring in a React app, is not installed by default in the project or has been removed. Since web-vitals is an optional package, you can safely resolve this issue by either installing the package or removing the code that imports it.
Option 1: Install the web-vitals package
If you want to keep the performance monitoring functionality and resolve the error, simply install the web-vitals package.
- In the terminal, navigate to your project folder (if not already there):
cd my-routing-app- Install
web-vitalsby running the following command:
npm install web-vitals- After installation is complete, restart the development server:
npm startThis should resolve the error, and your application should compile correctly.
Option 2: Remove the Web Vitals Code (If Not Needed)
If you don’t need performance monitoring and want to get rid of the error, you can safely remove the import and usage of web-vitals from your code.
- Open
src/reportWebVitals.jsand remove its contents or just comment out the code:
// import { reportWebVitals } from './reportWebVitals';
// You can safely remove the call to reportWebVitals or leave it commented out
// reportWebVitals();- Save the file, and the application should compile without the error. You can now continue developing your app.

good job