9. Design and implement C/C++ Program to sort a given set of n integer elements using Selection Sort method and compute its time complexity. Run the program for varied values of n> 5000 and record the time taken to sort. Plot a graph of the time taken versus n. The elements can be read from a file or can be generated using the random number generator.
Step 1: Implement the Selection Sort Algorithm
The Selection Sort algorithm works by repeatedly finding the minimum element from the unsorted part and putting it at the beginning.
PROGRAM:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
// Function to perform selection sort on an array
void selectionSort(int arr[], int n)
{
int i, j, min_idx;
for (i = 0; i < n-1; i++)
{
min_idx = i; // Assume the current element is the minimum
for (j = i+1; j < n; j++)
{
if (arr[j] < arr[min_idx])
{
min_idx = j; // Update min_idx if a smaller element is found
}
}
// Swap the found minimum element with the current element
int temp = arr[min_idx];
arr[min_idx] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
}
}
// Function to generate an array of random numbers
void generateRandomNumbers(int arr[], int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
arr[i] = rand() % 10000; // Generate random numbers between 0 and 9999
}
}
int main()
{
int n;
printf("Enter number of elements: ");
scanf("%d", &n); // Read the number of elements from the user
if (n <= 5000)
{
printf("Please enter a value greater than 5000\n");
return 1; // Exit if the number of elements is not greater than 5000
}
// Allocate memory for the array
int *arr = (int *)malloc(n * sizeof(int));
if (arr == NULL)
{
printf("Memory allocation failed\n");
return 1; // Exit if memory allocation fails
}
// Generate random numbers and store them in the array
generateRandomNumbers(arr, n);
// Measure the time taken to sort the array
clock_t start = clock();
selectionSort(arr, n);
clock_t end = clock();
// Calculate and print the time taken to sort the array
double time_taken = ((double)(end - start)) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
printf("Time taken to sort %d elements: %f seconds\n", n, time_taken);
// Free the allocated memory
free(arr);
return 0;
}Step 2: Measure Time Taken
The above program generates n random numbers, sorts them using the Selection Sort algorithm, and measures the time taken for the sorting process.
Step 3: Run the Program for Various Values of n
To collect data, run the program with different values of n greater than 5000, such as 6000, 7000, 8000, etc., and record the time taken for each.
Step 4: Plot the Results
You can use a graphing tool like Python with matplotlib to plot the results.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# data collected
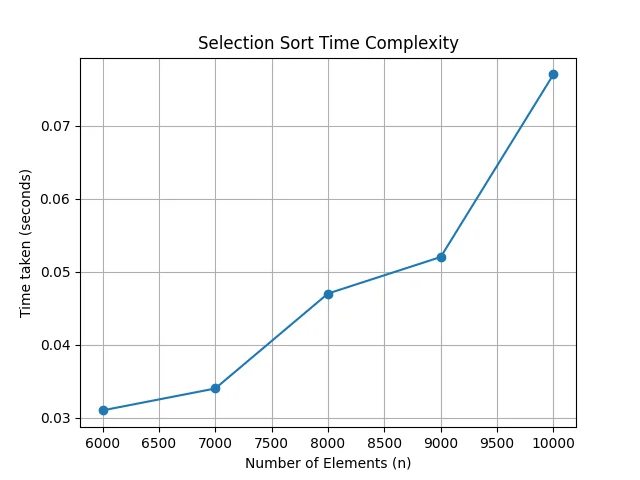
n_values = [6000, 7000, 8000, 9000, 10000]
time_taken = [0.031000, 0.034000, 0.047000, 0.052000, 0.077000] # replace with actual times recorded
plt.plot(n_values, time_taken, marker='o')
plt.title('Selection Sort Time Complexity')
plt.xlabel('Number of Elements (n)')
plt.ylabel('Time taken (seconds)')
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()OUTPUT:
Enter number of elements: 6000
Time taken to sort 6000 elements: 0.031000 seconds
********************************************************************
Enter number of elements: 7000
Time taken to sort 7000 elements: 0.034000 seconds
********************************************************************
Enter number of elements: 8000
Time taken to sort 8000 elements: 0.047000 seconds
********************************************************************
Enter number of elements: 9000
Time taken to sort 9000 elements: 0.052000 seconds
********************************************************************
Enter number of elements: 10000
Time taken to sort 10000 elements: 0.077000 seconds